Material selection
The Zund digital knife cutter has three methods for working with materials, drawing, cutting, and scoring. It can be used to work with any material that can be cut with a knife, but there are some that will work better than others. Materials are easier to cut if they are flexible and isotropic. Materials that are brittle, have a grain, or otherwise change significantly through a workpiece will be difficult to impossible to work with the Zund cutter. The standard blade that the School of Architecture keeps in the machine has a maximum cutting depth of 3/16” or 4.8mm. If you need to cut a material thicker than that, please see an AT staff member to have them install a specialty blade.
| Easy to work | Challenging to work | Do not cut |
| Chipboard | Cardboard (B-flute or thicker) | Wood (natural or engineered) |
| Museum board | Leather | Acrylic (plexiglass) |
| Paper | Fabric | Polycarbonate (Lexan) |
| Matboard | Acetate >0.5mm thick | Metal sheet |
| Pulp board | Soft metal foil | |
| Vinyl | Foamcore | |
| Acetate <0.5mm thick | Gatorboard | |
| Sytrene | Corrugated Plastic | |
| Urethane foam (open-cell) | ||
| EVA (vinyl foam) | ||
| Cardboard (C-flute - microflute) |
Assemble your geometry on 4 layers with the following names based on the role you want each type of geometry to have: Sheet, Draw, Score, and Cut.
Sheet This layer will contain the shapes that define your sheet boundaries. You don’t need to include these, but they can be very helpful, especially in laying out multiple sheets of material simultaneously.
Draw This layer’s geometry will be traced by the pen tool, which is by default a black ballpoint pen. Setting the exact thickness of your material will greatly improve the quality of drawn lines. Drawing with a material profile that is set too thick may keep the pen from making any contact with your material. If you want to use a different type of drawing tool, contact the AT staff.
Score Geometry on this layer will be traced by the knife, but only pierce a percentage of the way through your workpiece. That percentage will change depending on the type of material you select. If using a material that doesn’t appear in the default material library, please consult with AT staff.
Cut Geometry on this layer will trace out the path taken by the knife, piercing all the way through your workpiece. Thickness settings are not critical for this layer, but material profile selection will dramatically change performance. If you want to cut a material that isn’t in the default library, consult with AT staff.
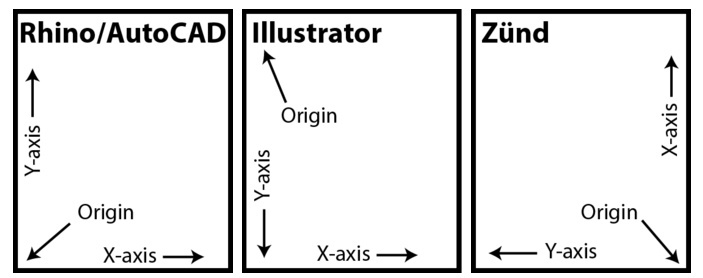
The X axis on the Zund is 48” long and the Y axis is 52” wide. These axes are oriented differently than most CAD/CAM systems. In the Zund software, the Y axis is the horizontal on the screen, the X axis is vertical, and the origin is in the bottom right corner. Geometry modeled in Rhino, AutoCAD, or Illustrator will appear to rotate counter-clockwise 90° when sending it to the Zund. Your geometry will look different on the screen, but it has not actually changed.
NOTE: Illustrator doesn’t treat its coordinate system in the same way as traditional CAD programs either. You’ll still see the 90° counter-clockwise rotation that you would from AutoCAD and Rhino, but the artboard will be ignored, and the origin and Y-axis will be changed.
Exporting geometry
Rhino
Regardless of the units you modeled your geometry in, change your units to millimeters. Select Yes if you are prompted to scale your geometry as a result of changing units. Even though the Zund software works in inches by default, it will interpret DXF files in millimeters.
Select your geometry and use the Export command. Choose the DXF file type.
Use the 2007 Natural export profile.
Drag the resulting DXF file into the Zund Drop folder located on the desktop.
AutoCAD
From the application menu click on Save As… > Other Formats.
Select the DXF filetype in the window that appears.
Drag the resulting file into the Zund Drop folder on the desktop.
Illustrator
Save your work as an AI file.
Drag the resulting file into the Zund Drop folder on the desktop.
Placing your material
Set your workpiece onto the bed. There’s no need to set them against the origin, but by default your geometry will be justified against the origin point. You can move it away from the origin by using CutEdit after pulling the job up in the CutQueue. You can place multiple sheets of material on the bed at once, but all the sheets must be of the same material and the same thickness. Trying to work with multiple thicknesses or material types simultaneously will cause poor results for at least one workpiece in the job.
NOTE: If you didn’t put your sheet boundary in your file, your geometry will be justified by default to the edge of the working are. Either move your geometry in CutEdit after loading it in the queue, or place your material at least half an inch past the X and Y axes. Cutting all the way to edge of your material, especially cutting straght lines that run parrallel to an edge of your workpiece, is very likely to shift your sheet during the cut.
Zund Knives/Knife Blades
PREV : What materials are best suited for the ZUND Z16 blades? Specifications and dimensions NEXT : Introduction Of The Performance Of Tungsten Steel Blades