What's The Difference Between A Digital Cutter | Cutting Systems | Flatbed Cutter Module, Tool And Blade?
A digital cutter system combines a programmable cutting platform with interchangeable blades, modules, and software to cut a wide range of materials, while a cutting system is the broader category that includes the entire machinery and workflow for preparing, routing, and finishing cut parts. A flatbed cutter module is a specific form factor within digital cutters designed to hold and cut flat, often rigid or thick, substrates. Tools and blades are the consumables and attachments that enable the actual cutting, creasing, scoring, perforating, or routing functions.
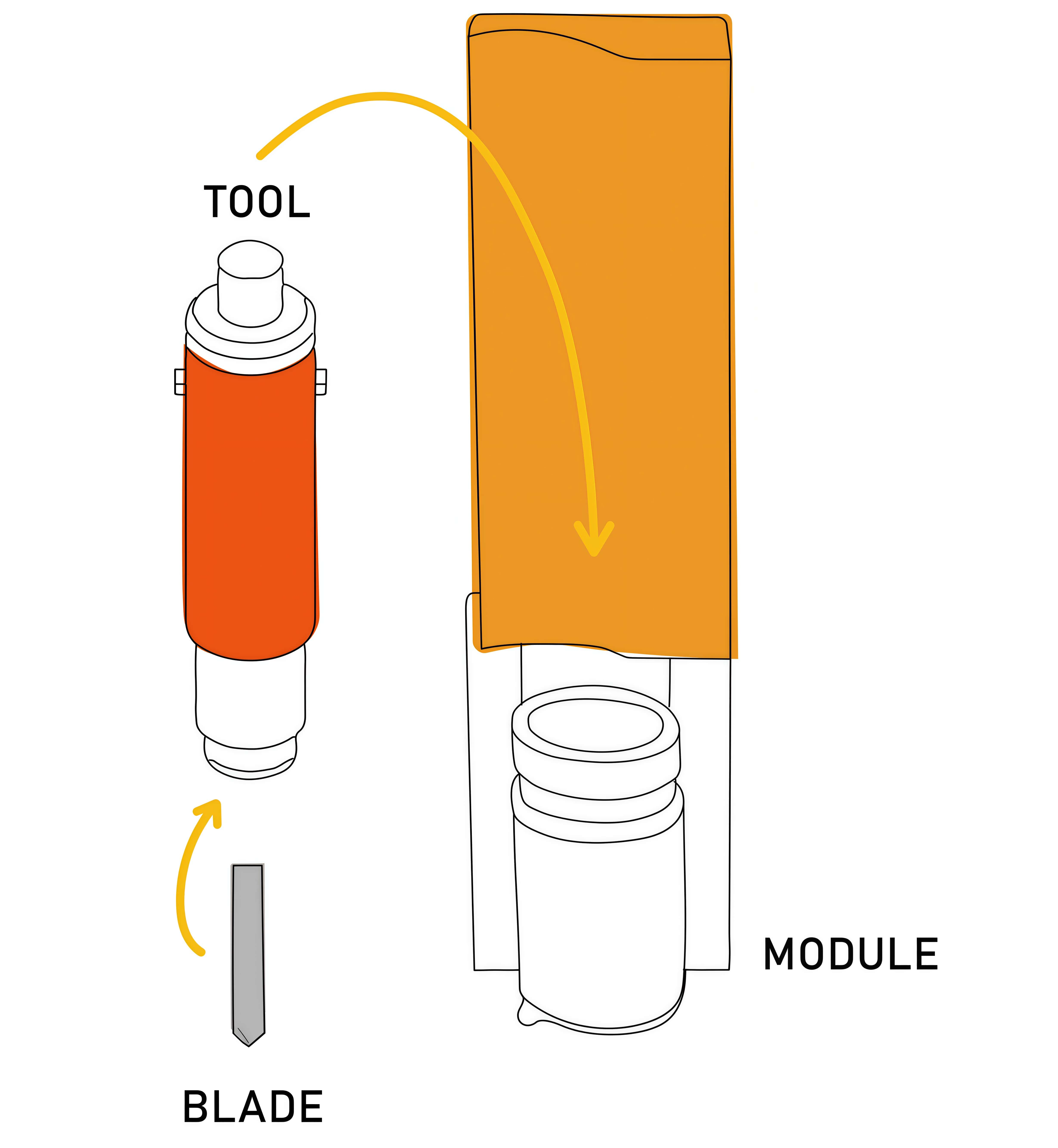
The Module attached to the machine and is used to hold the different tools. There are various types of modules that perform different functions e.g. routing or punching. At the Design Futures Lab we have a universal module which can hold most cutting tools.
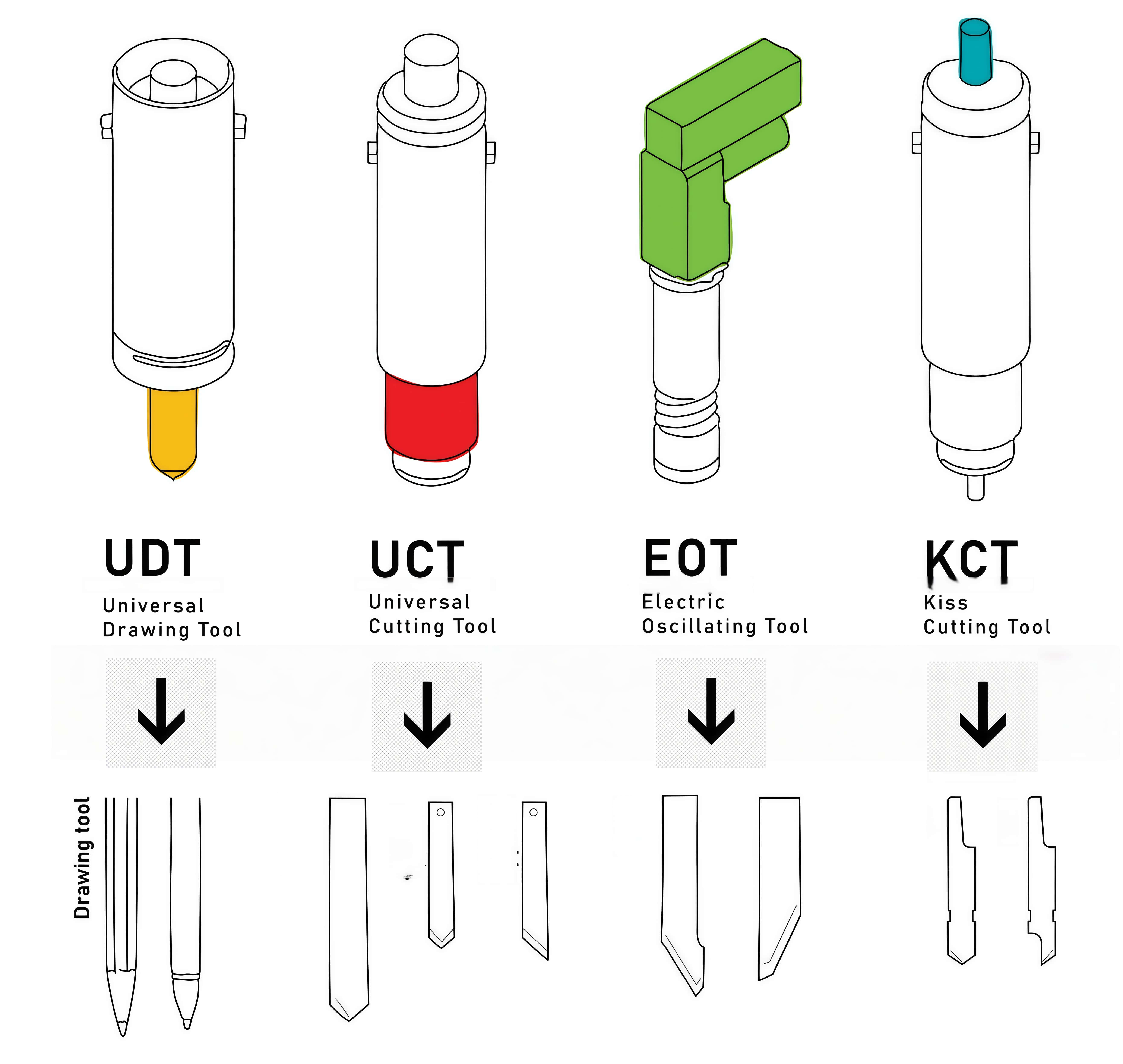
The Tool sits inside the module and is used to hold the blade, pen or wheel. Numerous different tools can be used in the universal module, each with different applications. At the Design Futures Lab we have a universal cutting tool, an electric oscillating tool, a kiss cutting tool and a universal drawing tool.
The Blade is held within the tool and is what is used to cut the material. Different blades are suited for different materials and can vary in size and shape. It is important to use the right blade for the material you wish to cut otherwise it can damage the tool and module.
Key distinctions and relationships
-
Digital cutter: An umbrella term for computer-controlled cutting devices that use blades, knives, or other tools to follow vector designs. It emphasizes digital control, software, tool changes, and modular configurations. It often supports multiple tool types and can cut a variety of materials, including flexible and some rigid substrates. Typical capabilities include contour cutting, kiss-cutting, perforation, and scoring, with software-driven precision.
-
Cutting system: The broader production setup that encompasses the digital cutter, feed and material handling, waste management, software, and post-cut processes. It includes the workflow from design to finished parts, plus any auxiliary equipment (e.g., routers, creasers, online conveyors).
-
Flatbed cutter module: A form factor and integration option within a digital cutter system optimized for flat, non-wrapping materials. It uses a rigid bed and a vertical cutting mechanism to achieve precise, high-quality cuts on thicker or rigid substrates. It is particularly suited for signage, packaging, textiles mounted on rigid boards, and similar applications where the material lies flat during cutting.
-
Tool and blade: The actual cutting implements mounted in the cutter head, chosen based on material and geometry. Blades are selected by material type (e.g., vinyl, film, cardboard, leather, carbon fiber composites) and cut method (straight blade, oscillating blade, drag blade, perforating tools, creasing tools, scoring blades, etc.). The tool/change system determines how quickly blades can be swapped to maintain productivity and accuracy.
Practical guidance for choosing
-
Material compatibility: Match blade type and cutting method to the material’s properties (flexible vs. rigid, thickness, fiber content, adhesives). Flatbed configurations excel with thicker or rigid substrates, while roll/offset configurations may be optimized for continuous, flexible materials.
-
Production needs: If high-precision, intricate cuts on rigid substrates are routine, a flatbed cutter with a robust tool assortment is advantageous. For high-volume, roll-fed materials, a roll or flatbed system with efficient tool changes can optimize throughput.
-
Modularity and upgrades: Look for a system that supports quick tool changes and a broad tool library (e.g., straight blades, drag blades, oscillating blades, creasing and scoring tools, routing bits) to maximize versatility across applications.
UCT - Known as a 'Drag' blade with a cutting motion similar to a scalpel. Used for cutting cardboard, paper and cardstock, polypropylene, rubber, PVC and canvas.
EOT - A motorised blade with a oscillating cutting motion good for soft or flexible materials. Can be used for cutting leather, foam-core, felt, rubber or textiles.
KCT - The variable pressure of the kiss-cut tool enables precise cutting of vinyl and film without damage to the liner material. Used for cutting adhesive vinyls.
PREV : About CNC Digital Cutting Systems & Flatbed Cutters Tools NEXT : Tools for For Digital Cutter | Cutting Systems | Flatbed Cutter