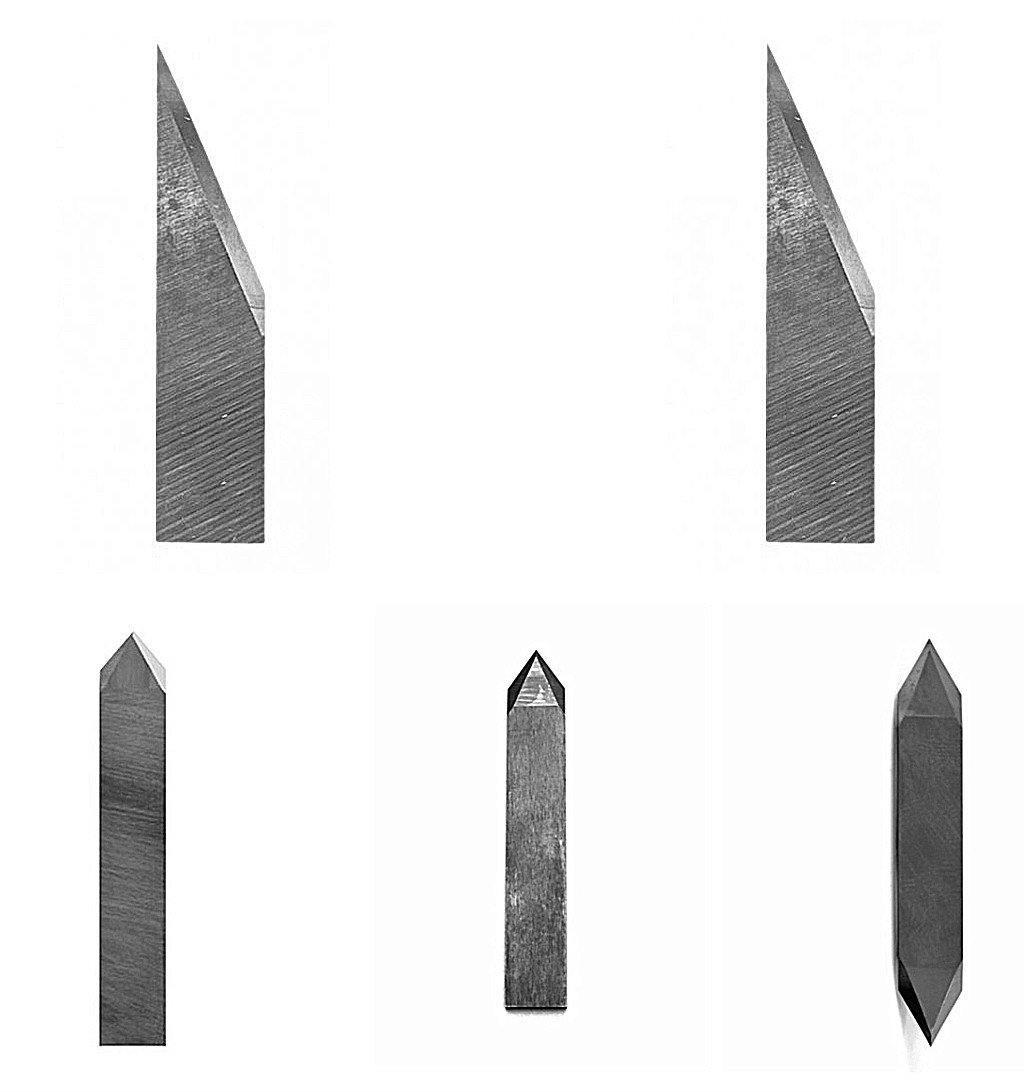
Here’s a detailed overview of Drag Knife Blades used for Zund, Esko Kongsberg, Summa, and other CNC digital cutters and plotters:
The drag knife blade is a specialized tool commonly utilized within digital cutting systems for precise and efficient material cutting. Unlike rotating blades, the drag knife operates as a static, non-rotating blade that is strategically offset to enhance cutting performance. This blade is designed to pivot freely, seamlessly adapting to changes in direction as it follows the movements of the cutting head. By dragging through the material rather than relying on a spinning motion, the drag knife offers controlled, accurate cuts, making it an essential component for tasks requiring detail and precision.
Key Features
Offset Tip Design: Allows the blade to pivot naturally while cutting curves.
Material: Usually made from tungsten carbide or high-speed steel (HSS).
Applications:
Vinyl
Films & foils
Cardboard/paper
Reflective sheeting
Soft foams
Textiles
Compatible Cutting Systems
Compatible Drag Knife Blade Examples
Zund: Z10, Z11, Z13, Z16, Z17 (with Drag Knife Tool - DKT, UCT)
Esko Kongsberg: BLD-SR6223, BLD-DR8160 (with Rigid or Flexi Tool)
Summa: 390-534, 390-560, 500-9800 series drag blades
Others Compatible with iEcho, Jwei, Aristo, Roland, Graphtec
Tips for Choosing the Right Blade
When selecting a blade for cutting applications, consider several key factors to ensure optimal performance and accuracy. The blade offset, typically measured in millimeters (such as 0.25 mm or 0.5 mm), plays a crucial role in determining the level of precision during cuts and the sharpness of corners. An incorrect offset can lead to poor-quality results or inconsistent cuts. The blade angle, defined by degrees (e.g., 30°, 45°, or 60°), is equally important, as it dictates the blade's ability to handle varying material thicknesses. A 30° blade is ideal for working with thin materials such as vinyl, ensuring clean and precise cuts. A 45° blade serves as a versatile choice for most standard cutting tasks and is typically suited for medium-thickness substrates. For tougher applications, such as cutting thick or laminated materials, a 60° blade offers enhanced durability and strength to maintain cutting effectiveness. Additionally, the shank diameter of the blade—commonly available in sizes like 2 mm, 3 mm, or 6 mm—must align with the size requirements of the tool holder to ensure compatibility and stability during use.
Proper Blade Replacement and Maintenance
Maintaining your blades is essential for achieving consistent performance and maximizing their lifespan. Drag knives are particularly prone to wear when used on abrasive materials, as the added friction can quickly degrade the blade's cutting edge. To ensure optimal functionality, always pair your blade with the appropriate tool module for your cutting system; for instance, Zund’s DKT-Universal module is specifically designed for certain applications and should be used accordingly to prevent mismatched configurations. When not in use, storing blades in protective cases is highly recommended to safeguard the delicate tips from accidental damage, such as bending or chipping. Proper maintenance practices not only help extend the longevity of your blades but also contribute to better output quality and reduced downtime during projects.
Shenzhen Oyea Global sales: ensuring availability across Europe, the USA, the Middle East, and Asia with efficient shipping and customer service.Sold To Germany, France, The United Kingdom, Poland, The United States, Russia, Vietnam, Thailand, Indonesia, Singapore, The Netherlands, Switzerland, South Korea, Japan, Turkey, The Philippines, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Italy, Spain, Hungary, The Czech Republic And Other Countries Or Regions
PREV : Summa Aristo Gerber Esko Roland Zund Knives And CNC Knife Blades Are Widely Sold And Distributed NEXT : Atom Kimla Polska Grupa Cnc Seron Tungsten Steel Blade Compatibility Replacement Applicable





